CWE Glossary
- CWE-22: Path Traversal
- CWE-78: OS Command Injection
- CWE-79: Cross-Site Scripting
- CWE-89: SQL Injection
- CWE-90: LDAP Injection
- CWE-91: XML Injection
- CWE-94: Code Injection
- CWE-98: PHP File Inclusion
- CWE-113: HTTP Response Splitting
- CWE-119: Buffer Errors
- CWE-130: Improper Handling of Length Parameter Inconsistency
- CWE-193: Off-by-one Error
- CWE-200: Information Exposure
- CWE-211: Information Exposure Through Externally-Generated Error Message
- CWE-236: Improper Handling of Undefined Parameters
- CWE-276: Incorrect Default Permissions
- CWE-284: Improper Access Control
- CWE-285: Improper Authorization
- CWE-287: Improper Authentication
- CWE-297: Improper Validation of Certificate with Host Mismatch
- CWE-306: Missing Authentication for Critical Function
- CWE-312: Cleartext Storage of Sensitive Information
- CWE-345: Insufficient Verification of Data Authenticity
- CWE-352: Cross-Site Request Forgery
- CWE-384: Session Fixation
- CWE-427: Uncontrolled Search Path Element
- CWE-434: Unrestricted Upload of File with Dangerous Type
- CWE-476: NULL Pointer Dereference
- CWE-521: Weak Password Requirements
- CWE-601: Open Redirect
- CWE-611: Improper Restriction of XML External Entity Reference ('XXE')
- CWE-613: Insufficient Session Expiration
- CWE-618: Exposed Unsafe ActiveX Method
- CWE-671: Lack of Administrator Control over Security
- CWE-798: Use of Hard-coded Credentials
- CWE-799: Improper Control of Interaction Frequency
- CWE-822: Untrusted Pointer Dereference
- CWE-835: Infinite Loop
- CWE-918: Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
- CWE-942: Overly Permissive Cross-domain Whitelist
CWE is a trademark of the MITRE Corporation.
Information Exposure Through Externally-Generated Error Message [CWE-211]
Information Exposure Through Externally-Generated Error Message describes information exposure case where software generates a message with potentially sensitive data and outputs it.
![Information Exposure Through Externally-Generated Error Message [CWE-211] Information Exposure Through Externally-Generated Error Message [CWE-211]](/images/vulnerability/previews/information-exposure-through-externally-generated-error-message-cwe-211.jpg)
Created: December 10, 2013
Latest Update: December 28, 2020
Table of Content
- Description
- Potential impact
- Exploitation Examples
- Severity and CVSS Scoring
- Mitigations
- References
- Latest Related Security Advisories
Want to have an in-depth understanding of all modern aspects of Information Exposure Through Externally-Generated Error Message [CWE-211]? Read carefully this article and bookmark it to get back later, we regularly update this page.
1. Description
This weakness describes information disclosure case where software performs an operation that triggers an error or diagnostic message in an external component. It is a child element of Information Exposure weakness and should be treated as such.
An example of this weakness is an error generated by the programming language interpreter used by software. The provided error message may contain potentially sensitive information and can be used to advance the attack surface.
This weakness can be introduced on design, implementation or operation stages of software development process and is not restricted to certain programming languages; PHP however is the most common and popular example.
The exposed information can be divided into two groups:
- Exposure of system information
e.g. file system structure, installation directory, installed software and its versions, etc. - Exposure of sensitive data
e.g. database structure, memory dump, login credentials, etc.
Exposure of error messages is often used to determine vulnerabilities that exist within the application, such as PHP File Inclusion, or SQL injection, and is helpful for performing advanced attacks against the application. Knowledge of web application document root is extremely valuable when exploiting PHP local file inclusions, since it is possible to determine possible log file location to include and execute PHP code stored in webserver log files.
2. Potential impact
An attacker might be able to gain access to restricted information and use it to widen the attack surface. Depending on the disclosed information, it might be possible to escalate privileges within the application or, in rare cases, to gain complete control over the system.
3. Exploitation Examples
Let's have a look at certain common cases of this weakness.
Example 1
The application uses incorrect credentials to connect to database. The error message generated by PHP exposes database user and database host:
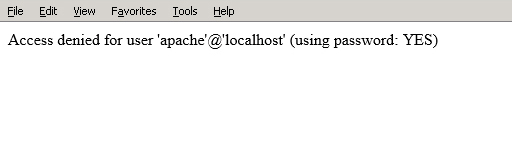
Example 2
The application uses the PHP "include()" function to include non-existent file. As a result, PHP generates an error message that includes full path to the application and certain system configuration.
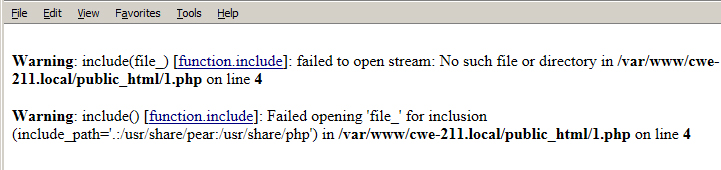
As we can see from examples above, the application outputs data that can be useful for an attacker to e.g. perform a brute-force attack or gain knowledge of file system structure.
4. Severity and CVSS Scoring
Here is a scoring example of installation path disclosure.
3.7 [CVSS:3.0/AV:N/AC:H/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:L/I:N/A:N] - Low severity.
Examples of this weakness:
Installation Path Disclosure Weakness in Flatnux
Installation Path Disclosure weakness in Tribiq CMS
5. Mitigations
The best way to protect your system against this weakness is to disable any output of error messages. Here are basic rules that should be followed when creating and implementing the application. Be sure that the application:
- does not generate errors accessible to others
- does not output debugging information
- handles errors internally and does not display errors that may contain potentially sensitive data
- sanitizes all input and does not send unverified data to external components that might trigger unhandled exceptions (e.g. division by zero, fatal errors).
The environment should be also configured not to output additional information.
PHP
Set the option "display_errors=0" in php.ini file or use PHP function error_reporting(0) to disable output of error messages. ASP
Use the following configuration in web.config.
- <configuration>
- <system.web>
- <customErrors mode="On" defaultRedirect="error.htm" />
- </system.web>
- </configuration>
Ruby
To disable error output run the server with the "-e production" option. Another way is to set "config.consider_all_requests_local=false" in application environment.
NodeJS
To disable verbose debugging messages set the NODE_ENV to production. This disallows stack traces from being returned upon error conditions.
set NODE_ENV=production 6. References
- CWE-211: Information Exposure Through Externally-generated Error Message [cwe.mitre.org]
- Full Path Disclosure [owasp.org]

